Services
 A treatment focusing on the science of movement, physiotherapy helps to restore, maintain, and monitor the function, motion, and well-being of physical issues. This physical therapy helps eliminate pain, improvise mobility, and recover from surgery or avoid surgery. It helps you in managing age-related issues and balances pain.
A treatment focusing on the science of movement, physiotherapy helps to restore, maintain, and monitor the function, motion, and well-being of physical issues. This physical therapy helps eliminate pain, improvise mobility, and recover from surgery or avoid surgery. It helps you in managing age-related issues and balances pain.
Rehabilitation as structured program of physical therapy focus on constant improvement of functional status of the patient. Rehabilitation helps to restore from chronic pain, surgery, accident, sports injury or any other damages. It reduces pain and helps you become active without causing discomfort or any suffering. It strengthens muscles and reduces the risks of falls or accidents. It helps restore mobility and speedy recovery of patient from illness or accident malfunction.
Structured exercise program to improve or maintain spinal mobility (stretching exercises) and stability (strengthening exercises) is all needed for patients with chronic back pain or postural related back pain.
 Spinal injections are used in two ways. First, they can be performed to diagnose the source of back, leg, neck, or arm pain (diagnostic). Second, spinal injections can be used as a treatment to relieve pain (therapeutic).
Spinal injections are used in two ways. First, they can be performed to diagnose the source of back, leg, neck, or arm pain (diagnostic). Second, spinal injections can be used as a treatment to relieve pain (therapeutic).
A special shot of injection can help relieve the immense pain immediately. They are 30 minutes day case procedures done under image guidance (fluoroscopy) and not as intense as spinal surgery. Instead, they are fast relieving and comparatively more effective than physical therapy.
There are several types of spinal injections targeting various pain sources and included those injected directly into the joints at the back of your spine (facet joint injection), spinal canal (epidural injection), around the nerve root (selective nerve root block) and into the disc (discogram), they are not as intense as spinal surgery. The injection decreases the swelling and pressure on large nerves around your spine relieving pain. For quick pain relief, a spinal injection is an excellent option.
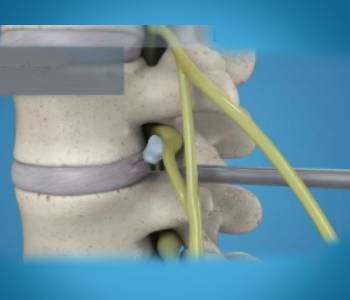 Discectomy is a surgical procedure performed to remove herniated disc material that is pressing on a nerve root or the spinal cord. Removal of the disc material will give immediate leg and back pain relief.
Discectomy is a surgical procedure performed to remove herniated disc material that is pressing on a nerve root or the spinal cord. Removal of the disc material will give immediate leg and back pain relief.
There are several ways through which surgeon can remove the herniated disc. Standard is open microdiscectomy, which uses a special microscope to view the disc and nerves. Less invasive (minimally invasive) way is removing the disc material through small tubes and microscope (micro-endoscopic discectomy). Least invasive way is Endoscopic Discectomy in
which disc material is removed through tiny incision less than little finger breadth with aid of special spinal endoscope allowing rapid recovery of the patient.
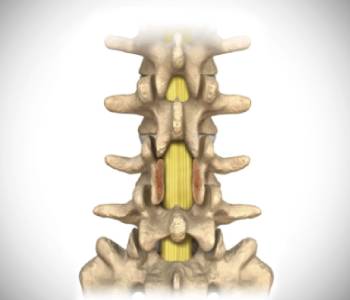 This surgical procedure involves removing the bone, bone spurs, and ligaments that are compressing the nerves. This procedure may also be called a “decompression.” This back or neck surgery surgery helps to relieve compression on the spinal cord or spinal nerves caused either by spinal stenosis, herniated disk, spondylosis, ossified posterior longitudinal ligament (OPLL), ossified ligamentum flavour(OLF),infection, tumours, injury or other compressive causes.
This surgical procedure involves removing the bone, bone spurs, and ligaments that are compressing the nerves. This procedure may also be called a “decompression.” This back or neck surgery surgery helps to relieve compression on the spinal cord or spinal nerves caused either by spinal stenosis, herniated disk, spondylosis, ossified posterior longitudinal ligament (OPLL), ossified ligamentum flavour(OLF),infection, tumours, injury or other compressive causes.
Laminectomy can be performed as open surgery using a single, larger incision to access your spine. Minimally invasive approach use smaller incision and tubular retractors without musch disruption of muscle mass with advantage of less post-operative pain and enhanced early functional recovery.
 Spinal fusion is a surgical procedure used to correct problems with the small bones in the spine (vertebrae). The basic idea is to fuse together two or more vertebrae so that they heal into a single, solid bone. This is done to eliminate painful motion or to restore stability to the spine.
Spinal fusion is a surgical procedure used to correct problems with the small bones in the spine (vertebrae). The basic idea is to fuse together two or more vertebrae so that they heal into a single, solid bone. This is done to eliminate painful motion or to restore stability to the spine.
Spinal fusion may help relieve symptoms of many back problems including degenerative disc disorder, herniated disks, spinal stenosis, spondylolysthesis (slipped vertebrae), infection, tumour, fracture, and deformities (scoliosis and kyphosis).
Lumbar interbody fusion is the commonly performed surgical procedure for variety of spinal disorders.When it comes to spine fusion there multiple approaches (Posterior/Transforaminal/Anterior/Lateral/Oblique) and there are many minimally invasive fusion options enhancing rapid recovery from surgery. Minimally invasive Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion (OLIF) is the least invasive fusion procedure.
 A lumbar disc replacement is suggested when you want to treat discogenic low back pain. It is recommended when your back pain comes from 1 or 2 discs in the lower spine, you have no joint disease or compression on the nerves of your spine or instability. Disc Replacement is an alternative to spinal fusion in selective cases.
A lumbar disc replacement is suggested when you want to treat discogenic low back pain. It is recommended when your back pain comes from 1 or 2 discs in the lower spine, you have no joint disease or compression on the nerves of your spine or instability. Disc Replacement is an alternative to spinal fusion in selective cases.
A cervical disc replacement is an alternative option to standard cervical fusion for patients with neck or arm pain due to cervical disc herniation. In artificial disc replacement, worn or damaged disk material between the small bones in the spine (vertebrae) is removed and replaced with a synthetic or “artificial” disk. The goal of the procedure is to relieve back pain while maintaining more normal motion than is allowed with some other procedures, such as spinal fusion.
The advantages of disc replacement over a fusion have been well studied. For appropriately selected patients, disc replacements maintain range of motion, less stress (wear and tear) at adjacent spinal levels and a lower rate of additional surgery.
 A revision surgery is a procedure to correct a previous operation that either failed to relieve pain from your initial condition or caused further internal complications due to a misdiagnosis, surgeon error, lack of fusion, infection, hardware malfunction, adjacent segment/level wear and tear or lack of recovery following a previous surgery. The spine is one of the most complex parts of your body affecting the functionality of both the skeletal and nervous systems with 33 small irregular shaped bones protecting the vital job of the spinal cord. This means that a spinal surgery complication is unfortunately a tricky situation and should be addressed by an experienced specialist in revision surgery.
A revision surgery is a procedure to correct a previous operation that either failed to relieve pain from your initial condition or caused further internal complications due to a misdiagnosis, surgeon error, lack of fusion, infection, hardware malfunction, adjacent segment/level wear and tear or lack of recovery following a previous surgery. The spine is one of the most complex parts of your body affecting the functionality of both the skeletal and nervous systems with 33 small irregular shaped bones protecting the vital job of the spinal cord. This means that a spinal surgery complication is unfortunately a tricky situation and should be addressed by an experienced specialist in revision surgery.
Revisiting a surgical site where there is already distress and complications is a very complex and multi-faceted surgical procedure and should be done by a specialist familiar with revision surgeries. There is several pain relieving procedures and corrective surgeries that can be done to improve pain, function and quality of life after previous failed back surgery. Revision spine surgery done after thorough evaluation and understanding of the problem along with careful pre-operative surgical planning, use of modern technology and skilled team yield excellent outcome comparable to successful primary spine surgery.
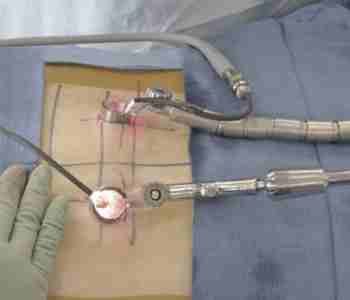 Spine surgery is traditionally done as “open surgery.” This means that the area being operated on is opened with a long incision to allow the surgeon to view and access the anatomy. In recent years, however, technological advances have allowed more back and neck conditions to be treated with a minimally invasive surgical technique.
Spine surgery is traditionally done as “open surgery.” This means that the area being operated on is opened with a long incision to allow the surgeon to view and access the anatomy. In recent years, however, technological advances have allowed more back and neck conditions to be treated with a minimally invasive surgical technique.
Because minimally invasive spine surgery (MISS), does not involve a long incision, it avoids significant damage to the muscles surrounding the spine. Typically, this results in less pain after surgery and a faster recovery.
The indications for minimally invasive spine surgery are the same as those for traditional open surgery. Minimally invasive spine surgery (MISS) is also called less invasive spine surgery. In these procedures, specialized instruments are used to access the spine through small incisions with less surgical insult to spinal musculature. Advantages of MISS include smaller incisions, less surgical bleeding, less post-operative pain, reduced post-operative pain killers, early mobilisation shorter hospital stay and early functional return to normal.
There are numerous minimally invasive techniques. The common thread between all of them is that they use smaller incisions and cause less muscle damage. Minimally invasive techniques can be used for common procedures like lumbar discectomy, decompression and spinal fusion.
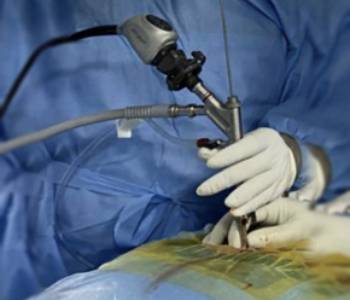 A procedure that has revolutionized the treatment of your back or leg pain, Endoscopic spine surgery utilizes small tubes through few millimetre long skin cuts which are assisted with a high-definition camera called an endoscope that provides panoramic vision of the internal surgical area. The process minimises tissue damage, blood loss, reduces pain, requires less medication, and helps in immediate recovery.
A procedure that has revolutionized the treatment of your back or leg pain, Endoscopic spine surgery utilizes small tubes through few millimetre long skin cuts which are assisted with a high-definition camera called an endoscope that provides panoramic vision of the internal surgical area. The process minimises tissue damage, blood loss, reduces pain, requires less medication, and helps in immediate recovery.
 Endoscopic spine surgery is an advanced, state-of-the-art form of minimally invasive spine surgery designed to provide the patient a quicker recovery time and less recurring pain than traditional spine surgery methods. ESS also can help preserve normal range of spine mobility post-operatively. In some cases, the ESS procedure can be performed using local anaesthesia instead of general anaesthesia, decreasing overall medical risks in patients who are older and/or have co-existing medical disorders that may increase surgical risk.
Endoscopic spine surgery is an advanced, state-of-the-art form of minimally invasive spine surgery designed to provide the patient a quicker recovery time and less recurring pain than traditional spine surgery methods. ESS also can help preserve normal range of spine mobility post-operatively. In some cases, the ESS procedure can be performed using local anaesthesia instead of general anaesthesia, decreasing overall medical risks in patients who are older and/or have co-existing medical disorders that may increase surgical risk.
 Robotic Spine Surgery integrates advanced computer technology with the experience of the skilled surgeons. This process is assisted by robots enabling surgeon to perform complex tasks with flexibility, precision, and control that is easier than conventional techniques.
Robotic Spine Surgery integrates advanced computer technology with the experience of the skilled surgeons. This process is assisted by robots enabling surgeon to perform complex tasks with flexibility, precision, and control that is easier than conventional techniques.
Robotic assistance transforms spine surgery from freehand procedures to highly-accurate and precise state-of-the-art procedures with less radiation. Robotic assistance is used in wide range of spine surgeries from complex reconstructions of scoliosis/kyphotic deformities to minimally invasive fusion surgeries for lower back disorders.
 Scoliosis is the problem causing the spine to curve abnormally, leading to twisted sideways on the coronal plane. Kyphosis is sagittal plane deformity where the spine curves forward abnormally (rounded or hunch back).
Scoliosis is the problem causing the spine to curve abnormally, leading to twisted sideways on the coronal plane. Kyphosis is sagittal plane deformity where the spine curves forward abnormally (rounded or hunch back).
Goals of scoliosis/kyphosis correction surgery are to stop the curve’s progression, reduce the deformity and maintain trunk balance. With the tools and technology available today, deformity trained skilled surgeon are able to achieve safe and desired correction of the deformity. Intra-operative neuromonitoring (IONM) is a technology will allows real time monitoring of spinal cord function/integrity during scoliosis/kyphosis deformity correction and this minimises the risk of intra-operative spinal cord injury.
The operation for kyphosis is a spinal fusion. The basic idea is to realign and fuse together the curved vertebrae so that they heal into a single, solid bone.
The options for scoliosis correction are standard long fusion, growing rod system and novel growth modulating non-fusion (fusion less) anterior vertebral body tethering.
Traditional Posterior Spinal Fusion corrective surgery permanently fuses two or more adjacent vertebrae so that they grow together at the spinal joint and form a solid bone that no longer moves. Modern surgical approaches and instrumentation—rods, screws, hooks, and/or wires placed in the spine—have enabled spinal fusion surgeries to achieve better curvature correction and faster recovery times than in the past. An advantage to spinal fusion surgery is that it has a long-term record of safety and efficacy for treating scoliosis. While a drawback to the procedure is that any fused vertebrae will lose mobility, which can limit some of the back’s bending and twisting, today’s spinal fusions tend to fuse fewer vertebrae and maintain more mobility than in the past.
Temporary Growing Rod (TGR) systems which aims to delay definitive fusion utilises rods anchored to the spine to help correct/maintain the spine’s curvature while the child grows. Every 6 to 12 months, the child has another minor day care procedure to lengthen the rods to keep up with the spine’s growth. Once the child is close enough to skeletal maturity, the child will usually get a definitive spinal fusion. If a spinal fusion is done at too young of an age (typically younger than age 10 in girls or less than 12 in boys), that could leave less room for the lungs to develop in addition to the child having an unusually short trunk compared to the limbs. To avoid these complications, the growing systems method helps guide the spine as it grows, preventing the curve from worsening as the spine matures and eventually becomes ready for a fusion if needed.
Novel Fusion less (Non Fusion) Scoliosis Correction Surgery uses growth modulation ability of the child spine similar to what has been done in the past to treat unequal leg heights in growing children. The theory is that by putting constant pressure on a bone, it will grow slower and denser. By applying such pressure on the outer side of a spinal curve, the surgeon aims to slow or stop the growth of the curve’s outer side while the curve’s inner side continues to grow normally. As the spine continues to grow in this manner, the lateral curvature should reduce as the spine becomes straighter.
Fusion less method uses anterior vertebral body tethering (AVBT) system, which involves placing screws on the outer side of the curve and then tensioning them taut with a cord so the spine straightens. Compared to spinal fusion, fusion less surgery has the potential benefit of retaining more spinal mobility and flexibility and being less invasive than standard posterior corrective spinal fusion procedures. However, this is a newer approach and long-term data about the risks and benefits are not yet available.
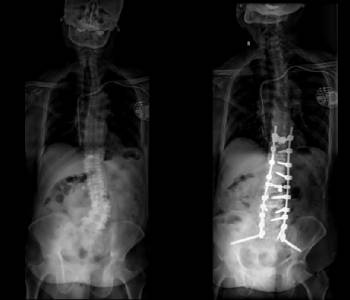 Spinal alignment and curvature can be altered in many ways. They can occur as a result of a birth defect, a child’s growth, aging, injury, or previous spine surgery. The most common type of spinal deformity in adults is degenerative scoliosis.
Adult spinal deformity defined as a deviation in the alignment of the spinal column of more than 10 degrees when viewed from the front, or a loss in normal curvature when viewed from the side – can have a major impact on quality of life. Symptoms may include significant pain and reduced function. Adult spinal deformity refers to a group of conditions in which the spinal column bends abnormally either to the right or to the left (degenerative scoliosis). It is commonly associated with a forward-bending posture and increased hunching of the upper back (Flat back). These deformities are end spectrum of degenerative (spondylotic) changes that happen in spine as we age.
Surgical options vary depending on the severity of the symptoms, the number of levels affected, the type of deformity, quality of bones (osteoporosis) and patient medical conditions (co-morbidities). A combination of different fusion and instrumentation techniques are used to treat the patient’s specific condition.
Spinal alignment and curvature can be altered in many ways. They can occur as a result of a birth defect, a child’s growth, aging, injury, or previous spine surgery. The most common type of spinal deformity in adults is degenerative scoliosis.
Adult spinal deformity defined as a deviation in the alignment of the spinal column of more than 10 degrees when viewed from the front, or a loss in normal curvature when viewed from the side – can have a major impact on quality of life. Symptoms may include significant pain and reduced function. Adult spinal deformity refers to a group of conditions in which the spinal column bends abnormally either to the right or to the left (degenerative scoliosis). It is commonly associated with a forward-bending posture and increased hunching of the upper back (Flat back). These deformities are end spectrum of degenerative (spondylotic) changes that happen in spine as we age.
Surgical options vary depending on the severity of the symptoms, the number of levels affected, the type of deformity, quality of bones (osteoporosis) and patient medical conditions (co-morbidities). A combination of different fusion and instrumentation techniques are used to treat the patient’s specific condition.